podcast 117 – The Son of God 1 – Dr. Lee Irons’s trinitarian view of Jesus
Dr. Lee Irons on his contribution to the new book The Son: Three Views of the Identity of Jesus, interview by Dr. Dale Tuggy for episode 117 of the trinities podcast.
Dr. Lee Irons on his contribution to the new book The Son: Three Views of the Identity of Jesus, interview by Dr. Dale Tuggy for episode 117 of the trinities podcast.
 Given my scholarly interests in Hinduism, I had to post a link to this story about the conversion of a Reformed Christian philosopher to a form of Hinduism.
Given my scholarly interests in Hinduism, I had to post a link to this story about the conversion of a Reformed Christian philosopher to a form of Hinduism.
Pictured here are Krishna and his lover Radha. I take it that in Sudduth’s form of Hinduism Krishna is an avatar of Vishnu. Other Hindus consider Krishna to be the high god himself.
There is much art celebrating the love of these two.
The story for me was a bit spoiled when I watched a documentary in which a Hindu, Indian man explained that (at least on some versions) Radha is married to another, and is Krishna’s aunt. Perhaps some would object that I’m not looking at it metaphysically enough. (Update – to be fair, some Hindu sources assert them to be unrelated and married – see comment #11 below.)
In another famous episode, Krishna charms a bunch of cow-herding ladies.
I’m curious to read more about Sudduth’s conversion. How does one get from Calvin’s all-determining triune deity to Vishnu? I wonder if it is by way of fairly mainstream trinitarian modalism…
Myself, as I read Sudduth’s interesting narrative of his conversion I’m not sure where, i.e. with what sort of Christianity, he was starting from. I too have taught the Gita in an academic setting, but I have not had experiences like this:
Around 4:20am (Friday morning) September 16th, I woke suddenly from a deep sleep to the sound of the name of “Krishna” being uttered in some wayRead More »Reformed Christian Philosopher Converts to Hinduism
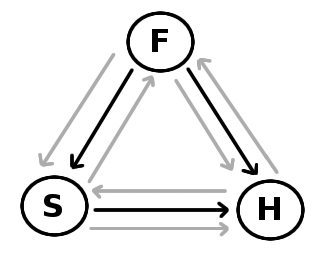
How the three are tightly functionally unified, in Swinburne’s view.
(See below for the interpretation.)
Last time we looked at Swinbure’s suggested reading of the creeds. They can’t he says, be charitably read as holding that in the same sense there’s only one divinity, and that there’s three. Swinburne comes down on the side of three. Like all social trinitarians, he’s attracted to a vision of the Trinity as being a loving community, three eternal and perfect, spirits, three selves, enjoying one another’s company, living in communion with one another, and working together in all they do. In short, he wants to say there are personal relationships internal to God – and this implies that there are persons – subjects of experience, thought, and action – in God.Read More »Swinburne’s Social Trinitarian Theory, Part 3 – functional monotheism
Is Ned in trouble? Here’s a quick post to wrap up the series on Brower’s and Rea’s constitution theory of the Trinity. First, it’s striking how original and self-consistent their approach is. It is rare to find something this new, and this well thought through on such an old topic. They’ve carefully carved out a unique position, one which has a motivation outside of theology… Read More »Constitution Trinitarianism Part 6: summing up
Continuing our survey from last time, fifth, sometimes “the Trinity is a mystery” means that the doctrine of the Trinity is unintelligible, or nearly so. Some ancient “church Fathers” hold that the doctrine of the Trinity can’t be literally understood, so that we’re forced to use analogies to describe it, all of which are very bad analogies. But, they seem to think, piling bad analogy upon… Read More »10 steps towards getting less confused about the Trinity – #3 Take the mystery out of appeals to “mystery” – Part 2
What is sometimes called the “Nicene Creed” and recited in churches is actually from this later council.
Last time, I mentioned a well done book by evangelical philosopher Gregg Ten Elshoff on the topic of self-deception and the Christian life. He noted that one may easily have a false belief about what one believes, and he noted that there can be strong social pressures to believe that one has beliefs one doesn’t (and that one lacks beliefs one in fact has). As… Read More »You’re Foolin’ Yourself and You Don’t Believe It – Part 2
 Three World Vision employees are fired because according to World Vision they don’t believe in that Jesus is “fully God” or that he’s a member of the Trinity.
Three World Vision employees are fired because according to World Vision they don’t believe in that Jesus is “fully God” or that he’s a member of the Trinity.
But inquiring minds want to know: what did they believe, what statement or statements of faith did they sign, and are the beliefs therein necessary and sufficient for being a real Christian? This time, we’re digging a little deeper.
Their website saith,
World Vision U.S. hires only those who agree and accept to its Statement of Faith and/or the Apostles’ Creed. (source)
Interesting! Note the “and/or” – employees must affirm either one or both. As we’ve noted before here at trinities, nothing in the so-called Apostles’ Creed requires belief in either the “full deity” of Christ (whatever that may mean) or any sort of trinitarian theory.Read More »No Trinity, No Job – Part 2
Most conservative (and even, many not-too conservative) Christians belong to churches and/or denominations which affirm traditional language about the Trinity. In this series, I’m going to just put all this on the table, as the fact is, many Christians, especially those from less “confessional” traditions, aren’t very familiar with these traditional formulas. I’m not going to go too much into the history for now. The… Read More »The Orthodox Formulas 1: The Council of Nicea (325)
This time, another great Christian thinker, who I discovered some time around 1998.
“The” doctrine of the Trinity was established neither at Nicea (325 AD) nor at Constantinople (381 AD). In catholic lore, it is all supposed to hang on the then novel term homoousios – but it does not – that is, not only on that. This one catholic Trinity doctrine is in fact not a fully determinate doctrine at all, but only a template, a set… Read More »Mark Edwards on Councils and the Trinity
 In this last post in this series, I want to put out a few critical reactions to Baber’s “Neo-Sabellian” Trinity theory.
In this last post in this series, I want to put out a few critical reactions to Baber’s “Neo-Sabellian” Trinity theory.
My thanks to Harriet for this piece and for her interaction with us here.
No doubt, she’ll argue back; and she will probably say something about how her views have changed since she wrote this piece.
So, in no particular order:
Just starting to think about the Trinity, as a Masters student.
 In a recent post I put forward my own preferred version of “Leibniz’s Law,” or more accurately, the Indiscernibility of Identicals. It’s a bit complicated, so as to get around what are some apparent counterexamples to the simpler principle which is commonly held.
In a recent post I put forward my own preferred version of “Leibniz’s Law,” or more accurately, the Indiscernibility of Identicals. It’s a bit complicated, so as to get around what are some apparent counterexamples to the simpler principle which is commonly held.
Aside for non-philosophers: philosophers are usually after universal principles, truths which hold in all cases, rather than mere non-universal generalizations, i.e. rough rules of thumb which have exceptions. (An example of the latter: Boys love trucks.) Thus, when a philosophers makes a (universal) claim, other philosophers come along and try to show that it is false with “counterexamples” – real, or even merely possible, examples which show the principle to be false (as it doesn’t apply to them). For example, if someone says that all Texans love tacos, a counterexample to this would be a person who is from Texas and doesn’t like them. Just one counterexample is enough to show a universal claim to be false. When provided with a counterexample, of course, one will often refine, as it were, the original claim (e.g. All native Texans love tacos, or All Texans who appreciate Tex-Mex food love tacos) and the game goes on. This is all in the interest of discovering together what is true and what is false. (In my example, of course, those “refinements” would admit of easy counterexamples too.)
So my principle said, to paraphrase, that for any x and y, x just is (=) y, only if they don’t ever intrinsically differ. (I put this in terms of one having a “mode” at a time if and only if the other also has that mode at that time. Others would call these “intrinsic properties.”)
Here our friend, philosopher and blogger Brandon offered a counterexample, Read More »On an alleged counterexample to Leibniz’s Law – Part 1

Of all the ancient catholic “fathers” I’ve read, Origen (c.185-254) is the most impressive as a scholar.
It’s not that I usually agree with him – any non-Platonist is going to choke on many of the dishes he’s serving, and I think that most today would take issue with some his ways of interpreting the Bible. But he has vast knowledge, he makes pretty careful distinctions, he knows how to argue, and is just a much more developed and original thinker than most. Any contemporary who was going to square off with him either did or should have considered him a formidable opponent.
He wrote, or rather dictated, a vast amount – evidently, he did little else. Some think he may have been the most prolific person in antiquity. We still have a fair number of texts from him.
He’s historically important for many reasons, but for this post, what’s most important is that in the 3rd century he was considered a stalwart of mainstream (“catholic”, or “proto-orthodox”) Christianity.
Lately I’ve been reading Origen’s Commentary on John, as translated by Ronald E. Heine, who by way, I have found very helpful. He too is a first-rate scholar.
Evidently, passage here is directed against certain monarchians who thought (or at least, were alleged to think) that the Father = the Son, i.e. that the Son is the Father himself and vice versa. This passage struck a nerve with me, as it reminded me of conversations I’ve had.
The references in brackets are from Heine’s footnotes.Read More »Origen: the Son is not the Father
In Part 1 I explained how vague it is to say that there are three divine Persons “in” God. In Part 2, I described some different things one might mean by “Persons”. In this third part, I’ll explain some of many things it might mean to say that the three persons are one “substance” (Greek: ousia, Latin: substantia). But before I do that, it is… Read More »“the” Trinity doctrine – Part 3