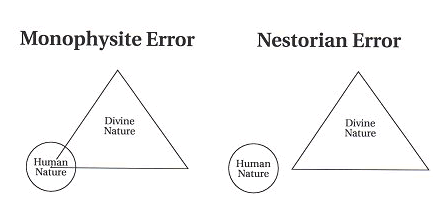
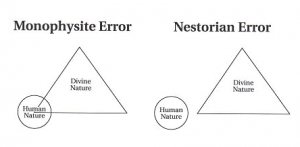
SCORING THE BURKE – BOWMAN DEBATE – ROUND 5 – BOWMAN – PART 3
 As I explained in the previous installment, in round 5 Bowman is trying to show that not only does the Bible imply that all three Persons are divine, but also that they in some sense are the one God. In other words, he wants to show how the NT brings the three, as it were, within the being of the one God.
As I explained in the previous installment, in round 5 Bowman is trying to show that not only does the Bible imply that all three Persons are divine, but also that they in some sense are the one God. In other words, he wants to show how the NT brings the three, as it were, within the being of the one God.
To do this, he considers a dozen triadic passages, in which the Three are all mentioned together in quick succession. Last time, I mulled over his treatment of the “Great Commission” passage. This time, a few others, and I take a crack at another explanation of this triadic language.
First, as I look at Bowman’s interpretations, some of them strongly suggest that he thinks that asserting the divinity of each just is asserting each to be numerically identical to God. I looked into this more last time, but briefly, this won’t fly, as it’ll make the persons identical to one another. So it is not clear, even if his expositions are right, that really support an orthodox Trinity theory.
Second, I reiterate that Bowman does a good job here, assembling a dozen important passages, in which it is impossible to ignore the triadic language. Suppose the doctrine of the Trinity is just this vague claim: “there are three co-equal persons in God”. If that is true, that would explain why these three are often mentioned together, in a way which can suggest they are on an equal footing. I said last time that any unitarian is obligated to explain these triadic statements in a way which is both compatible with unitarianism, and which is independently motivated (in can’t be that the only appeal of the reading is that it saves one’s theology).
Here’s Bowman’s treatment of one such text:Read More »SCORING THE BURKE – BOWMAN DEBATE – ROUND 5 – BOWMAN – PART 3


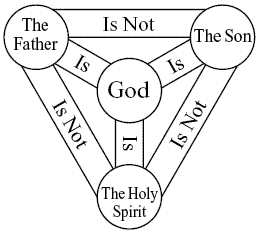


 In
In 

 In this post I venture to offer some debate advice: be very hesitant to accuse your opponent of a logical fallacy.
In this post I venture to offer some debate advice: be very hesitant to accuse your opponent of a logical fallacy.
 In my judgment, somewhat. Here’s an overview of his case, with some critical comments, and at the end I score the round.
In my judgment, somewhat. Here’s an overview of his case, with some critical comments, and at the end I score the round.