SCORING THE BURKE – BOWMAN DEBATE – Burke 2
 There’s a lot of meat in Burke’s second round, and both his and Bowman’s second rounds were cleaner, more free of stray punches than round 1. Here I offer some summaries and brief comments on Burke.
There’s a lot of meat in Burke’s second round, and both his and Bowman’s second rounds were cleaner, more free of stray punches than round 1. Here I offer some summaries and brief comments on Burke.
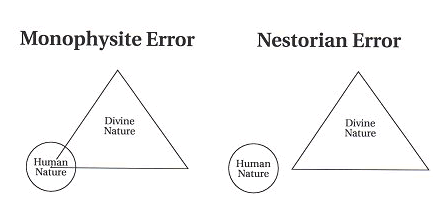
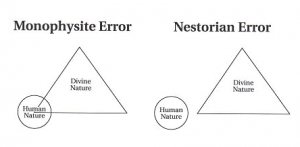
- In a lot of the piece, Burke lays out his positive views about Jesus. This should give a lot of people pause; it is often assumed, contrary to the long but largely forgotten history of this minority report, that unitarians are mere “deniers”, or that they can be lumped together with the amorphous “skeptics” who appear in apologetics writings, or that they are theological “liberals”, or that they are Unitarian Universalists. Not so – arguably, Burke affirms all the really obvious doctrines of the New Testament – messiah, mediator, resurrection, atonement, etc. – roughly, all the items in the “Apostles'” Creed. Burke defends what used to be called a “humanitarian” christology – that Jesus was a human, and did not exist before his miraculous conception in Mary. It would be misleading to describe his position as being that Jesus was “just a man”. In Burke’s view, he’s far from being just a “great teacher” among many, with peers like the Buddha and Muhammad, or even being merely a prophet.
- It is striking to what degree Burke simply ignores some influential (but now largely forgotten) patristic ideas, to wit: the Jesus’ ministry obviously manifested the divine nature (through, e.g. his miracles), that Jesus must be divine so as to be able to divinize humanity, that Jesus and not the Father was the one who interacted with the Jews in OT times, that the title “Son of God” implies having the divine nature, that what is “divine” must be absolutely unchanging and simple. I say this more by way of observation than criticism. With the exception of the first, I expect that Bowman will largely ignore them as well.
- Flag: Burke says that the risen, glorified Jesus isRead More »SCORING THE BURKE – BOWMAN DEBATE – Burke 2