Derivation vs. Generic Theories – part 6: Issues for the Generic View (JT)

“And the best thing is, we can take these blocks apart!”
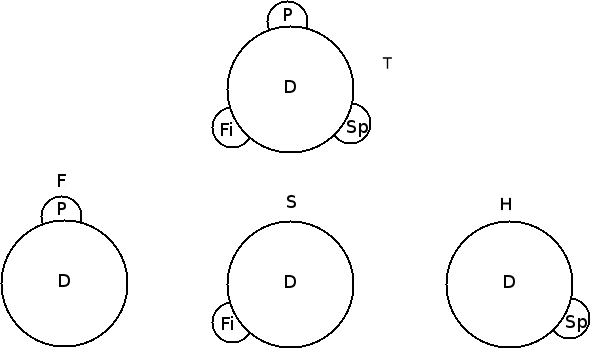
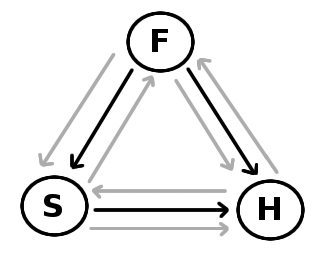
In the last post, I introduced the ‘generic view’ of the trinity, namely the claim that Divinity (that which makes the divine persons God/divine) is shared equally by all three persons and so does not belong to any one divine person more than another. In this post, I would like to highlight some of the issues faced by a generic view.
My point of departure is modern day criticism of the generic view such as that of Colin Gunton and John Zizioulas (to name just a few). These authors are not, in my opinion, the most philosophically astute critics, but nevertheless, they do highlight some of the issues relevant for the generic view.
Read More »Derivation vs. Generic Theories – part 6: Issues for the Generic View (JT)